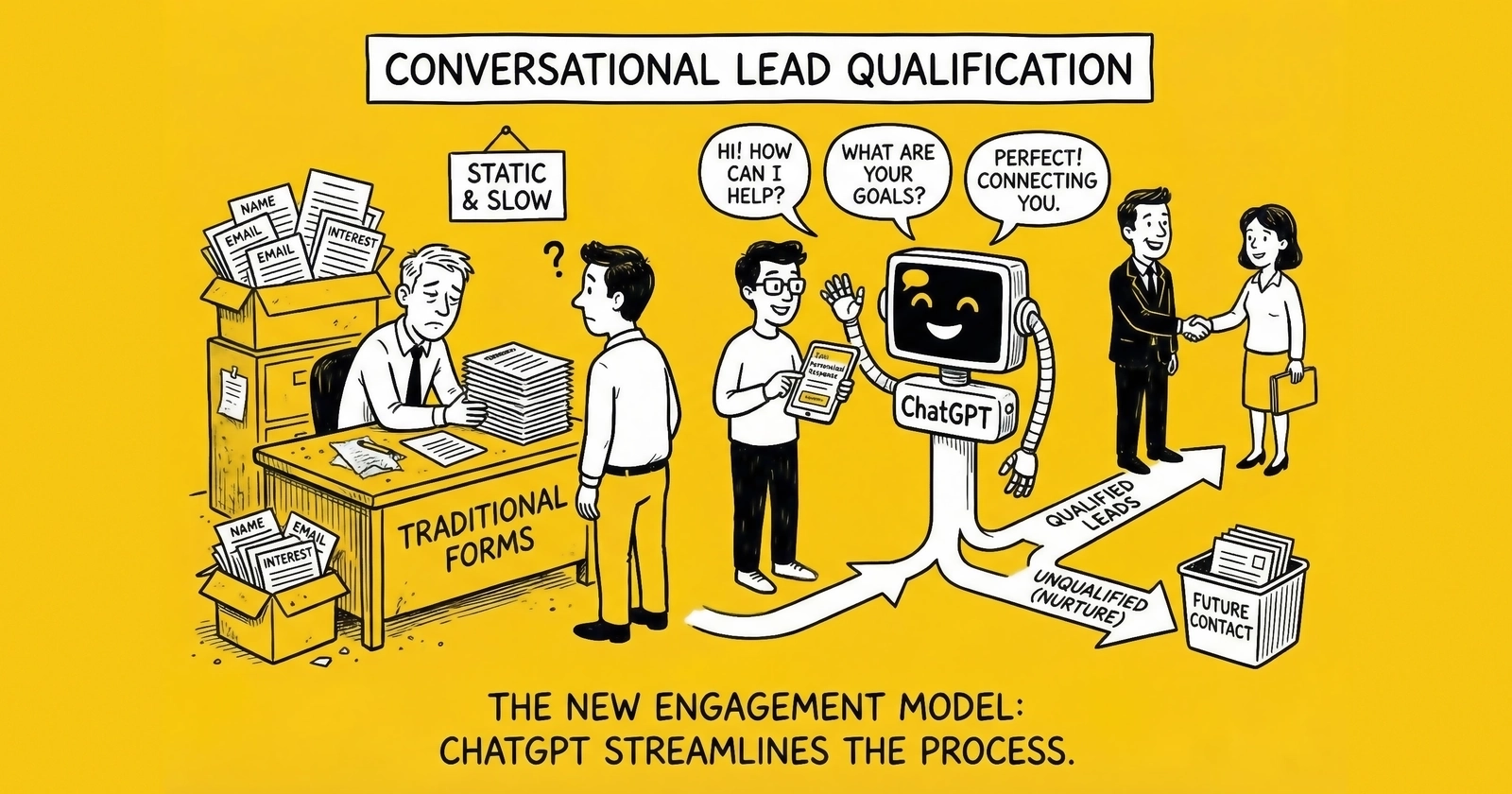
The moment a prospect submits a form, a timer starts. Every minute that passes without meaningful engagement, conversion probability decays. Industry data shows leads contacted within one minute convert at 391% higher rates. This is the essence of speed to lead in lead generation. Yet most organizations take hours or days to respond – if they respond at all.
Conversational AI, led by large language models like ChatGPT, has fundamentally altered this equation. What previously required expensive human labor now happens in milliseconds. The initial qualification conversation – determining whether a lead deserves human attention – can occur instantly, 24 hours a day, at a fraction of traditional cost.
Sixty-seven percent of consumers now prefer self-service options over speaking with company representatives. Seventy-four percent expect immediate responses when they contact businesses. Chatbots handle these expectations at scale, with properly implemented conversational AI achieving 30% increases in qualified lead generation and reducing cost-per-qualified-lead by 40-60%.
But the gap between conversational AI promise and operational reality remains vast. Most implementations fail to capture potential value because they treat ChatGPT as a chatbot replacement rather than a qualification system redesign. They deploy without proper prompt engineering, integration architecture, or human handoff protocols.
This guide examines how conversational AI actually transforms lead qualification – from the technical architecture required for effective deployment to the conversation design principles that separate high-performing implementations from expensive disappointments. We cover the real economics, the implementation pitfalls, the integration requirements, and the strategic positioning that determines whether conversational qualification becomes your competitive advantage or an expensive experiment.
The Qualification Problem Conversational AI Solves
Understanding why conversational AI matters requires understanding the lead qualification problem it addresses.
The Economics of Traditional Qualification
Traditional lead qualification operates on human labor. A sales development representative reviews incoming leads, makes phone calls, sends emails, and determines which prospects warrant senior sales attention. This approach has fundamental constraints.
Labor cost per qualification attempt ranges from $8-25 depending on geography and skill level. A skilled SDR handles 40-60 meaningful qualification conversations daily. After accounting for no-answers, voicemails, and dead ends, perhaps 15-25 leads receive actual qualification each day.
Response time suffers because humans work in shifts. Leads arriving at 11 PM wait until 9 AM. Weekend submissions wait until Monday. International leads face timezone mismatches that can delay response by 12-24 hours.
Quality varies with individual SDR skill, motivation, and workload. The conversation that happens at 4:45 PM on Friday differs from the conversation at 9:15 AM on Tuesday. Training consistency helps but cannot eliminate human variance.
Scale creates impossible choices. Double your lead volume and you must double your SDR headcount – or accept that half your leads receive no timely qualification. Most organizations accept the latter, writing off leads that could have converted with proper attention.
The Qualification Velocity Gap
The gap between lead arrival and meaningful qualification represents pure value destruction.
Research from multiple industry sources converges on a consistent finding: lead conversion probability drops by approximately 10% for every hour of delay. A lead worth $100 in the first hour is worth $90 in the second hour, $81 in the third, and so on. After 24 hours of delay, that lead retains perhaps 25% of its original value.
Yet average response time across industries ranges from 42 hours to never. Studies consistently show that 37-50% of inbound leads never receive any follow-up contact. These are not low-quality leads that should be ignored – they are leads that arrived when nobody was watching and fell through the cracks.
Conversational AI closes this gap. When a form submission triggers an immediate qualification conversation, the velocity gap shrinks from hours to seconds. The 10%-per-hour decay becomes negligible because engagement happens instantly.
The Qualification Quality Problem
Beyond speed, traditional qualification suffers from consistency problems that conversational AI can address.
Human qualifiers ask different questions in different orders, interpret answers inconsistently, and make subjective judgments that vary across individuals and moods. One SDR considers a prospect “budget-ready” while another would classify the same prospect as “early stage.”
Information capture varies similarly. Some SDRs meticulously document conversation details. Others log minimal information, losing context that would improve downstream conversion.
These inconsistencies compound at scale. When qualification quality varies by 30-40% across individuals, marketing cannot accurately assess lead source quality, sales cannot reliably forecast conversion, and optimization becomes guesswork.
Conversational AI executes the same qualification protocol every time. Questions arrive in consistent sequences. Answers are captured in structured formats. Classification follows defined logic rather than individual judgment. This consistency enables optimization that inconsistent human execution prevents.
How ChatGPT Changes the Qualification Equation
ChatGPT and similar large language models represent a step-function improvement over previous chatbot generations. Understanding this distinction matters for implementation decisions.
Beyond Decision Trees
Previous chatbot generations operated on decision trees. If the user says X, respond with Y. If the user says Z, respond with W. These systems handled narrow paths effectively but failed when conversations deviated from anticipated flows.
Users quickly learned to recognize – and resent – these limitations. Questions outside the decision tree received irrelevant responses. Natural language variation confused the system. The experience felt mechanical, frustrating, and unhelpful.
Large language models fundamentally differ. They generate responses based on context understanding rather than pattern matching. When a prospect asks an unexpected question, the system can formulate a reasonable response rather than defaulting to “I don’t understand.”
This capability enables genuine conversation rather than guided form-filling. Prospects can express themselves naturally, ask clarifying questions, and explore tangentially before returning to the qualification path. The experience feels like conversation with a knowledgeable assistant rather than navigation through a phone tree.
The Conversational Qualification Workflow
Effective ChatGPT qualification follows a structured workflow disguised as natural conversation.
Greeting and context establishment. The conversation opens by acknowledging the prospect’s inquiry and establishing the AI’s role. Transparency about AI involvement builds trust and sets appropriate expectations.
“Hi Sarah, thank you for your interest in comparing auto insurance rates. I’m an AI assistant here to help you find the best coverage options. I’ll ask a few quick questions to understand your situation, then connect you with the right specialist. This typically takes about 2-3 minutes. Does that work for you?”
Primary qualification questions. The system gathers essential information that determines lead routing and priority. These questions map to your qualification framework – BANT, MEDDIC, or custom criteria appropriate to your business.
For insurance leads, primary questions might include current coverage status, policy renewal timing, coverage types needed, and household composition. For mortgage leads: property type, purchase timeline, estimated credit range, down payment availability.
Information enrichment. Beyond minimum qualification requirements, the conversation gathers additional data points that enhance lead value. Phone number confirmation, email verification, preferred contact times, specific concerns or questions – each additional verified data point increases lead utility for downstream conversion.
Routing determination. Based on qualification responses, the system determines appropriate next steps. High-intent leads with strong qualification signals receive immediate callback scheduling or live transfer. Medium-intent leads enter accelerated nurture sequences. Low-intent or unqualified leads receive appropriate alternative resources rather than consuming sales capacity.
Handoff execution. The transition from AI to human must feel seamless. Context gathered during AI conversation transfers to the human representative so the prospect does not repeat information. The human understands qualification status, key concerns, and preferred communication style before the conversation begins.
Response Quality and Prompt Engineering
ChatGPT response quality depends heavily on prompt engineering – the instructions and context provided to shape its behavior.
Effective qualification prompts include:
Role definition. “You are a helpful assistant for [Company Name] specializing in [product/service]. Your goal is to understand visitor needs and determine if they’re a good fit for our solutions.”
Behavioral guidelines. “Be friendly but professional. Keep responses concise – typically 1-3 sentences. Ask one question at a time. Do not make promises about pricing or specific outcomes.”
Qualification criteria. “Determine these key factors: timeline (immediate, 1-3 months, just researching), budget authority (decision maker, influencer, researcher), current solution (none, competitor, existing customer), and specific pain points.”
Guardrails. “If asked about pricing, explain that pricing depends on individual circumstances and a specialist can provide accurate quotes. If the conversation veers off-topic, acknowledge politely and redirect. Never claim to be human.”
Response format. “After each response, internally assess qualification status: Qualified (ready for sales), Developing (needs more information), or Unqualified (poor fit). Include this assessment in your internal notes but not in the customer-facing response.”
The difference between adequate and excellent prompt engineering often determines whether conversational qualification succeeds or fails. Organizations achieving strong results invest significant time in prompt refinement, testing variations against real conversation transcripts, and iterating based on outcomes.
Implementation Architecture: Building the Technical Foundation
Conversational qualification requires more than ChatGPT access. Effective implementation demands integration architecture that connects AI conversation to your lead management infrastructure.
The Integration Stack
A complete conversational qualification system includes several components working together.
Conversation interface. The front-end where prospects interact – web chat widget, SMS conversation, or voice interface. This layer handles message rendering, typing indicators, and user experience elements.
LLM processing layer. The ChatGPT API (or alternative) that generates responses based on conversation context and qualification prompts. This layer manages API calls, handles rate limits, and processes responses.
Context management. A system tracking conversation state, accumulated information, and qualification status across multiple message exchanges. Without proper context management, each message exchange starts fresh, losing accumulated understanding.
Integration middleware. Connections to your CRM, lead distribution system, calendar scheduling, and other operational tools. When qualification completes, relevant data must flow to appropriate systems automatically.
Human handoff infrastructure. Mechanisms for routing qualified conversations to human representatives with full context. This might include live chat transfer, callback scheduling, or lead assignment to sales queues.
Analytics and monitoring. Tracking conversation outcomes, identifying failure patterns, measuring qualification rates, and capturing data for continuous improvement.
ChatGPT API Implementation Considerations
Using ChatGPT for conversational qualification requires understanding API characteristics that affect implementation decisions.
Latency. API response time varies from 1-10 seconds depending on prompt complexity, response length, and system load. For real-time chat, this latency requires UX accommodation – typing indicators, “thinking” states – that set appropriate expectations.
Token limits. Each API call has context window limits. Long conversations approaching these limits require summarization strategies that compress previous exchanges while preserving essential context.
Costs. API pricing based on tokens (roughly 4 characters per token) means conversation cost scales with length. A typical qualification conversation might consume 2,000-4,000 tokens, costing $0.02-0.08 depending on model tier. At scale, these costs accumulate but remain far below human qualification costs.
Rate limits. API rate limits affect high-volume implementations. Production systems need queuing, retry logic, and potentially multiple API keys to handle concurrent conversation volume.
Model selection. ChatGPT offers multiple model tiers with different capability/cost tradeoffs. GPT-4 provides superior reasoning and instruction-following for complex qualification scenarios. GPT-3.5-turbo handles simpler qualification flows at roughly 10% the cost. Many implementations use GPT-4 for high-value lead segments and GPT-3.5 for higher-volume, simpler qualification.
CRM and Lead Distribution Integration
Qualification data must flow to operational systems to generate value.
Real-time lead creation. When conversation captures lead information, that data should create or update records in your CRM immediately. Delayed batch processing loses the speed advantage that makes conversational qualification valuable.
Field mapping. Conversation data points must map to appropriate CRM fields. Define clear mappings before implementation: “Timeline” conversation responses map to “Purchase Timeframe” picklist values in Salesforce, “Budget” responses map to “Budget Range” fields, and so forth.
Qualification status transfer. AI qualification assessment should transfer to CRM as structured data, not just conversation transcripts. When a lead arrives at sales, the qualification status should be immediately visible without reading transcript history.
Lead distribution triggers. For organizations using lead distribution platforms (boberdoo, LeadsPedia, Phonexa), qualification completion should trigger distribution workflows. High-qualification leads route to premium buyers or priority sales teams. Medium-qualification leads route to appropriate nurture programs.
Conversation transcript logging. Full conversation transcripts should attach to lead records for context, quality assurance, and compliance documentation. These transcripts often prove valuable for training sales representatives on prospect concerns and language.
Human Handoff Mechanisms
The transition from AI to human represents a critical success factor. Poor handoffs negate the value that AI qualification creates.
Live transfer. For high-intent leads, real-time transfer to available human representatives maximizes conversion. This requires understanding current availability, routing to appropriate skill groups, and providing context before the human connects.
Scheduled callback. When no human is immediately available, the AI schedules a specific callback time that matches both prospect and representative availability. Calendar integration enables automatic scheduling rather than requiring manual coordination.
Lead assignment. For asynchronous follow-up, the AI assigns qualified leads to appropriate representatives with priority flags based on qualification strength. The representative receives notification with qualification context enabling immediate informed outreach.
Context transfer. In all handoff scenarios, the receiving human needs qualification summary, key concerns expressed, and any specific commitments made during AI conversation. The prospect should not repeat information already provided.
Escalation handling. When prospects explicitly request human assistance during AI conversation, the system must accommodate gracefully. Having escalation paths prevents frustration and demonstrates that AI serves prospect needs rather than creating barriers.
Conversation Design: What Actually Works
Technical implementation enables conversational qualification. Conversation design determines whether it works effectively.
Opening the Conversation
First impressions shape entire interactions. Effective opening messages accomplish multiple objectives simultaneously.
Acknowledge the trigger. Reference what brought the prospect to the conversation. “I see you’re interested in comparing home insurance rates” validates that the system understands their intent.
Establish identity. Transparency about AI involvement builds trust and sets appropriate expectations. “I’m an AI assistant here to help you find the right coverage” prevents later frustration when the prospect realizes they are not speaking with a human.
Preview the process. Brief explanation of what happens next reduces uncertainty. “I’ll ask a few quick questions to understand your situation – typically takes about 2 minutes – then connect you with the right specialist.”
Invite participation. End with a question or confirmation that invites response. “Does that work for you?” or “Ready to get started?” establishes the conversational dynamic.
Example opening:
“Hi there. I noticed you’re looking for solar installation quotes. I’m an AI assistant that helps connect homeowners with qualified installers in their area. I’ll need to ask a few quick questions about your home and energy usage – takes about 3 minutes. Then I can show you what incentives you qualify for and connect you with top-rated installers. Sound good?”
Asking Qualification Questions
Question design significantly impacts response quality and completion rates.
One question at a time. Multi-part questions confuse AI interpretation and frustrate prospects. “What’s your current coverage and when does it renew?” should become two separate questions.
Closed questions for clarity. When specific answers are needed, closed questions generate cleaner data. “Are you the primary decision-maker for insurance purchases in your household?” generates more useful data than “Tell me about your role in insurance decisions.”
Open questions for insight. When exploring concerns or motivations, open questions reveal information that structured questions miss. “What prompted you to start looking at solar now?” surfaces motivations that inform sales approach.
Natural language, not form language. Questions should feel conversational, not like reading form fields aloud. “When are you hoping to purchase?” works better than “What is your anticipated purchase timeline?”
Progression from easy to sensitive. Build rapport before asking sensitive questions. Name and basic situation first. Budget and timeline questions after establishing conversation flow. Credit or income questions only when necessary and after explaining why.
Handling Unexpected Responses
Prospects do not follow scripts. Effective systems handle deviation gracefully.
Off-topic questions. When prospects ask questions outside the qualification scope, acknowledge helpfully before redirecting. “That’s a great question about how solar affects home value – something our specialists can address in detail. To make sure I connect you with the right person, can you tell me approximately how much your monthly electric bill runs?”
Ambiguous responses. When answers are unclear, ask clarifying follow-ups rather than making assumptions. “I want to make sure I understand – when you say ‘soon,’ are you thinking in the next month or two, or more like the next quarter?”
Objections and concerns. When prospects express hesitation, acknowledge before continuing. “I understand – nobody wants to feel rushed into a decision. Just so you know, there’s no obligation at any point. My goal is just to understand if our solution might be a good fit for your situation.”
Requests for human assistance. Always accommodate. “Of course – let me connect you with a specialist who can help directly. Based on what you’ve shared, I can route you to someone who works specifically with situations like yours. One moment.”
Closing the Qualification
How conversations conclude affects both qualification accuracy and prospect experience.
Summarize understanding. Reflect back key points to confirm accuracy. “Just to make sure I have this right – you’re looking at full coverage for a 2018 Honda Accord, currently with State Farm, and your policy renews next month. Did I get that correct?”
Set clear expectations. Explain exactly what happens next. “Based on what you’ve told me, I can see three installers in your area with availability this week. Would you prefer morning or afternoon appointments?”
Confirm contact details. Verify the best way to reach them. “Is [phone number] still the best number to reach you? And do you have any preference on call versus text?”
Thank and transition. Close warmly while maintaining momentum. “Perfect. A solar specialist will call you this afternoon between 2 and 4 PM to discuss your options in detail. They’ll have all the information you’ve shared with me. Thanks for taking the time – talk soon.”
The Real Economics: What Conversational Qualification Actually Costs
Understanding true costs enables accurate ROI calculation and appropriate implementation decisions.
Direct API Costs
ChatGPT API pricing varies by model tier:
GPT-4 Turbo. Approximately $0.01 per 1,000 input tokens and $0.03 per 1,000 output tokens. A typical qualification conversation consuming 3,000 total tokens costs roughly $0.05-0.08.
GPT-3.5 Turbo. Approximately $0.0005 per 1,000 input tokens and $0.0015 per 1,000 output tokens. The same conversation costs roughly $0.002-0.004.
At volume, these differences matter significantly. An operation qualifying 10,000 leads monthly:
- GPT-4: $500-800/month in API costs
- GPT-3.5: $20-40/month in API costs
Model selection should match qualification complexity. Simple intent confirmation works fine with GPT-3.5. Complex multi-step qualification with nuanced judgment benefits from GPT-4.
Integration and Infrastructure Costs
API costs represent a fraction of total implementation expense.
Chat widget or interface. Commercial solutions (Intercom, Drift, custom builds) range from free tiers to $500+/month depending on features and volume. Custom development requires 40-100 engineering hours depending on requirements.
Integration middleware. Connecting ChatGPT to CRM, lead distribution, and other systems requires development effort. Estimate 60-200 hours for initial integration, depending on system complexity and API availability.
Prompt engineering and testing. Developing effective qualification prompts requires iteration. Budget 20-40 hours for initial development, plus ongoing optimization time.
Monitoring and analytics. Custom dashboards for conversation analytics require development investment or subscription to analytics platforms.
Ongoing maintenance. API changes, prompt updates, integration maintenance, and issue resolution require ongoing attention. Budget 5-10 hours monthly for mature implementations.
Comparison to Human Qualification
The relevant comparison is human qualification cost, not abstract cost-per-conversation calculations.
Human SDR qualification costs:
- Fully-loaded SDR cost: $5,000-8,000/month (salary, benefits, overhead)
- Qualification conversations per day: 15-25 (accounting for no-answers, research time, admin)
- Cost per successful qualification: $10-25
Conversational AI qualification costs:
- Fixed infrastructure: $500-2,000/month (depending on scale and sophistication)
- Variable API costs: $0.01-0.10 per conversation
- Cost per successful qualification: $0.50-5.00 (depending on volume)
At sufficient volume (typically 500+ leads monthly), conversational AI qualification costs 80-95% less than human qualification while providing 24/7 coverage and instant response.
2025 Chatbot Market Performance Benchmarks
The chatbot and conversational AI market has reached significant scale, providing reliable performance benchmarks:
Market Scale:
- Chatbot market: $15.57 billion (2025) → $46.64 billion (2029)
- 63% of B2B companies use chatbots for lead qualification
- 88% of users had at least one chatbot conversation in 2025
Conversion Performance:
- Chatbots achieve up to 70% conversion rates in some industries (vs 2-5% for traditional forms)
- Lead qualification time drops by 61% with automated workflows
- 55% of businesses report increase in high-quality leads
- 67% increase in sales for businesses using chatbots
- 3x higher conversion rates vs traditional forms in multiple studies
- $8 ROI for every $1 invested in chatbot development
Technical Capabilities (2025):
- NLP accuracy for top bots: 93%
- Sentiment analysis improves satisfaction by 19%
- Context-awareness reduces repeated questions by 30%
- AI chatbots retain conversation memory for up to 12 turns
These benchmarks represent industry-wide averages. Your implementation results will vary based on audience, use case, and execution quality.
ROI Calculation Framework
Return on investment depends on qualification volume, current conversion rates, and the value of qualified leads.
Baseline metrics needed:
- Current leads per month
- Current qualification rate (leads that receive timely qualification)
- Current conversion rate (qualified leads to customers)
- Customer lifetime value
Improvement assumptions:
- Qualification rate improvement (typically 40-80% increase from 24/7 instant response)
- Conversion rate improvement (typically 15-30% from improved qualification quality and speed)
- Cost reduction (typically 50-80% reduction in qualification labor costs)
Example calculation:
Current state:
- 1,000 leads/month
- 40% receive qualification (400 qualified)
- 20% of qualified convert (80 customers)
- $1,000 LTV per customer
- Monthly revenue: $80,000
- Qualification cost: $6,000/month (3 SDRs, partial time)
With conversational AI:
- 1,000 leads/month
- 85% receive qualification (850 qualified)
- 25% of qualified convert (212 customers)
- $1,000 LTV per customer
- Monthly revenue: $212,000
- Qualification cost: $1,500/month (AI infrastructure plus 1 SDR for escalations)
Net improvement: $132,000 additional monthly revenue, $4,500 cost savings.
These numbers represent strong outcomes. Conservative implementations might show 25-50% of these improvements. The directional case remains compelling even at reduced expectations.
Common Implementation Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Having observed dozens of conversational AI implementations, patterns emerge in what causes success and failure.
Mistake 1: Treating ChatGPT as a Chatbot
Organizations often deploy ChatGPT using the same approach they used for previous-generation chatbots – rigid flows, narrow scopes, minimal context. This wastes the capability that makes LLMs valuable.
The symptom: Conversations feel mechanical despite using advanced AI. Prospects encounter “I’m sorry, I can’t help with that” responses frequently. Qualification rates disappoint expectations.
The solution: Design for conversation, not for form-filling. Provide rich context in prompts. Allow flexible conversation paths that achieve qualification objectives without requiring specific question sequences. Test with adversarial users who deviate from expected paths.
Mistake 2: Inadequate Prompt Engineering
Many implementations use minimal prompts – a few sentences describing the AI’s role – and expect excellent results. ChatGPT is powerful but not telepathic. Without detailed instruction, it makes assumptions that may not match your requirements.
The symptom: Inconsistent response quality. Sometimes the AI asks great questions; sometimes it misses obvious follow-ups. Qualification assessments seem arbitrary. The AI makes promises or claims you would not approve.
The solution: Invest in comprehensive prompt development. Include explicit examples of good and bad responses. Define guardrails specifically. Test prompts against edge cases. Budget 20-40 hours for initial prompt development and expect ongoing refinement.
Mistake 3: Missing Integration Architecture
Deploying a chat widget with ChatGPT connection but no CRM integration creates an impressive demo that generates no business value. Qualification data that does not reach operational systems cannot inform action.
The symptom: Leads are “qualified” but the information does not appear in sales workflow. Representatives ask prospects to repeat information. No clear handoff process exists. Analytics are limited to chat tool native reporting.
The solution: Design integration architecture before deploying conversation interface. Define field mappings, handoff triggers, and context transfer mechanisms. Build or configure integration before launching to customers. Accept that integration work often exceeds conversation design work.
Mistake 4: Poor Handoff Experience
The transition from AI to human often destroys value that AI qualification created. Prospects repeat information, wait in queues, or receive callbacks that feel disconnected from their prior conversation.
The symptom: Prospects express frustration at handoff. Conversion rate improvement falls short of qualification rate improvement. Sales representatives ignore AI qualification notes because they find them unhelpful.
The solution: Design handoff as carefully as you design AI conversation. Ensure context transfer is immediate and complete. Brief receiving representatives on how to use AI-gathered information. Test handoff experience from prospect perspective, not just technical function.
Mistake 5: No Feedback Loop for Improvement
Implementations deployed without measurement infrastructure cannot improve. When you do not know which conversations succeed and which fail, optimization is impossible.
The symptom: Qualification rates plateau after initial deployment. The same problems recur. No data supports prompt refinement decisions. Leadership cannot assess whether the investment is generating returns.
The solution: Build measurement into initial implementation. Track conversation completion rates, qualification rates, handoff success, and downstream conversion. Connect qualification events to CRM outcomes. Review conversation transcripts systematically to identify failure patterns. Budget ongoing time for prompt refinement based on data.
Mistake 6: Ignoring User Experience Fundamentals
Advanced AI cannot overcome poor user experience fundamentals. Slow load times, confusing interfaces, unexpected behaviors, and mobile incompatibility undermine even excellent conversation design.
The symptom: High conversation initiation rates but low completion rates. Users abandon mid-conversation. Mobile users complain about usability. Chat widget conflicts with other page elements.
The solution: Apply standard UX principles. Test across devices and browsers. Monitor load times and interaction latency. Ensure chat interface does not obstruct critical page content. Watch real user sessions (with appropriate consent) to identify friction points.
Privacy, Compliance, and Disclosure Requirements
Conversational AI introduces compliance considerations that require attention.
Disclosure Requirements
Most jurisdictions require disclosure when consumers interact with automated systems. The specific requirements vary, but the principle is consistent: consumers should know they are communicating with AI.
Effective disclosure occurs early – in the opening message – and uses clear language. “I’m an AI assistant” works better than euphemisms like “virtual representative” that obscure the nature of the interaction.
Some states (California, for example) have explicit chatbot disclosure requirements. Even where not legally mandated, disclosure builds trust and sets appropriate expectations.
Data Collection and Privacy
Conversational qualification collects personal information subject to privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA, state privacy laws). Standard privacy practices apply:
Purpose limitation. Collect information needed for qualification, not everything the AI could potentially gather.
Consent. Ensure appropriate consent for data collection, particularly for information beyond basic contact details.
Data retention. Define retention periods for conversation transcripts and qualification data. Implement deletion processes for data past retention requirements.
Access rights. Enable consumer access to their data and conversation history as required by applicable regulations.
Security. Protect collected information with appropriate technical and organizational measures.
Recording and Monitoring
Conversation transcripts constitute records that may have compliance implications.
For industries with specific recordkeeping requirements (financial services, insurance), conversational AI transcripts may need to be retained and accessible for regulatory examination.
Call recording laws in two-party consent states (California, Florida, etc.) typically address audio recording, not text chat. However, the principle of transparency applies – consumers should understand that conversations are logged.
TCPA Considerations
Conversational AI qualification that transitions to outbound calling triggers TCPA compliance requirements.
Prior express written consent remains required for autodialed or prerecorded calls to mobile phones. AI qualification conversation that captures phone numbers must include appropriate consent language if you intend to call those numbers using automated systems.
The consent itself can be captured within the conversational interface, but the language must meet FCC requirements for specificity and clarity. Though the FCC’s one-to-one consent rule was vacated by the Eleventh Circuit in January 2025, generic “I agree to be contacted” language may not satisfy buyer requirements, as many sophisticated buyers require specific seller identification.
Measuring Success: The Metrics That Matter
Effective measurement enables optimization. Define key performance indicators before deployment and establish baseline comparisons.
Conversation-Level Metrics
Initiation rate. Percentage of eligible page visitors who begin conversations. Benchmark: 3-8% for proactive triggers, 15-30% for form-initiated chat.
Completion rate. Percentage of started conversations that reach qualification conclusion (either qualified, disqualified, or escalated). Benchmark: 60-80% for well-designed implementations.
Qualification rate. Percentage of completed conversations classified as qualified for sales follow-up. This varies dramatically by traffic quality – expect 20-40% for cold traffic, 50-70% for warm traffic.
Escalation rate. Percentage of conversations requiring human intervention. Benchmark: 10-20% for mature implementations. Higher rates suggest prompt improvement opportunities.
Average conversation length. Messages exchanged and time to completion. Track for optimization but recognize that “shorter” is not always better – thorough qualification may require more interaction.
Satisfaction indicators. Direct feedback (if requested) or proxy measures like conversation completion, return visits, and downstream conversion.
Business Impact Metrics
Response time improvement. Compare time-to-first-meaningful-contact before and after implementation. This is often the largest value driver.
Cost per qualified lead. Total qualification costs (infrastructure, API, remaining human costs) divided by qualified leads. Compare to pre-implementation cost.
Qualified lead volume. Total qualified leads per period. Should increase due to 24/7 coverage and instant response.
Downstream conversion rate. Conversion of qualified leads to customers. Should improve due to better qualification quality and faster response.
Revenue per conversation. Revenue attributed to customers originated through conversational qualification divided by total conversations. Ultimate measure of business impact.
Diagnostic Metrics
Failure pattern analysis. Categorize unsuccessful conversations by failure mode: abandonment, disqualification, escalation, technical failure. Prioritize improvement efforts based on frequency and addressability.
Question completion rates. Track which qualification questions get answered and which lead to abandonment. Questions with high abandonment warrant redesign.
Response quality scoring. Sample conversation transcripts and evaluate response quality against defined criteria. Identify systematic prompt improvement opportunities.
Time of day performance. Compare metrics across hours and days. Performance variation may reveal segment-specific optimization opportunities.
Advanced Implementations: Beyond Basic Qualification
Organizations achieving strong results from basic conversational qualification can extend capabilities further.
Multi-Channel Qualification
ChatGPT-powered qualification can extend beyond web chat to SMS, voice, and messaging platforms.
SMS qualification. Similar conversation flow delivered via text message. Advantages: reaches mobile users who prefer texting, maintains conversation across sessions, integrates with mobile-first audiences. Considerations: shorter message length constraints, carrier filtering, additional compliance requirements.
Voice AI. ChatGPT-powered voice conversations using speech-to-text and text-to-speech layers. Advantages: natural interaction for prospects who prefer phone, qualification during call rather than as precursor to call. Considerations: latency challenges, accent/speech recognition limitations, higher technical complexity.
Messaging platforms. WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and similar platforms enable conversational qualification within apps prospects already use. Advantages: familiar interface, existing notification infrastructure. Considerations: platform-specific APIs, content restrictions, integration complexity.
Personalized Qualification Paths
Advanced implementations customize qualification flow based on prospect characteristics.
Segment-specific prompts. Different qualification questions and conversation styles for different audience segments. Enterprise prospects receive different qualification than small business. Returning visitors receive different treatment than first-time visitors.
Behavioral adaptation. Conversation style adjusts based on prospect behavior patterns. Quick responders receive faster-paced qualification. Thoughtful responders receive more elaboration.
Progressive profiling. For known prospects with existing data, qualification focuses on gaps rather than recapturing known information. “I see you inquired about auto coverage last month – are you still considering the same vehicles?”
Integration with Intent Data
Combining conversational AI with intent data platforms creates powerful qualification enhancement.
Intent-informed opening. When intent data indicates prospect research behavior, opening messages can reference that context. “I noticed you’ve been researching coverage options for growing families – would you like to discuss how our plans handle life changes?”
Priority routing. High-intent signals from external data can elevate qualification priority and handoff urgency. Prospects showing strong buying signals receive immediate escalation to live representatives.
Qualification acceleration. For prospects with high intent scores, abbreviated qualification flows capture essential information without extensive discovery. Intent data has already established qualification status.
Predictive Qualification Scoring
Machine learning models can score qualification conversations in real-time, predicting conversion likelihood based on conversation patterns.
Conversation signals. Question count, response length, sentiment indicators, objection frequency, engagement patterns – all become predictive features.
Hybrid scoring. Combine AI conversation assessment with traditional lead scoring signals (source, demographics, behavior) for comprehensive conversion prediction.
Dynamic routing. Route leads based on predicted conversion value rather than simple qualified/not-qualified classification. High-value predictions receive premium handling.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does ChatGPT compare to traditional chatbots for lead qualification?
Traditional chatbots follow decision trees – rigid paths that break when prospects deviate from expected inputs. ChatGPT understands context and generates appropriate responses to unexpected questions, enabling genuine conversation rather than guided form-filling. In qualification scenarios, this translates to 40-60% higher completion rates and more accurate qualification assessment because prospects can express themselves naturally rather than fitting responses to narrow options.
What does conversational AI qualification cost per lead?
Direct API costs range from $0.002 (GPT-3.5) to $0.08 (GPT-4) per qualification conversation. Including infrastructure, integration, and maintenance, total cost per qualified lead typically ranges from $0.50-5.00 – compared to $10-25 for human SDR qualification. The cost advantage increases with volume as fixed infrastructure costs amortize across more conversations.
Can ChatGPT completely replace human qualification?
ChatGPT effectively handles 70-85% of qualification conversations without human intervention. The remaining cases – complex situations, explicit requests for human assistance, edge cases, and high-value prospects warranting personal attention – still benefit from human handling. The optimal model combines AI for efficiency and scale with humans for complexity and relationship building.
How do I handle prospects who want to speak with a human?
Always accommodate human escalation requests immediately. Design escalation paths that connect prospects with appropriate humans quickly while transferring conversation context. The AI should never become a barrier between prospects and human assistance. Tracking escalation frequency helps identify prompt improvements that could reduce unnecessary escalations while respecting legitimate requests.
What privacy and disclosure requirements apply to AI qualification?
Most jurisdictions require disclosure of AI involvement – “I’m an AI assistant” stated clearly in opening messages. Data collection during qualification is subject to standard privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA, state privacy laws). Conversation transcripts may have retention requirements depending on industry. If qualification leads to outbound calling, TCPA consent requirements apply.
How long does implementation typically take?
Minimum viable implementation – chat widget connected to ChatGPT API with basic qualification flow – can deploy in 2-4 weeks. Production-quality implementation with CRM integration, proper handoff protocols, comprehensive prompt engineering, and analytics typically requires 6-12 weeks. The primary timeline drivers are integration complexity and prompt optimization iteration cycles.
What qualification completion rates should I expect?
Well-designed conversational qualification achieves 60-80% completion rates – meaning 60-80% of prospects who begin the conversation complete it to a qualification conclusion. Lower rates typically indicate prompt issues (confusing questions, poor handling of objections), UX problems (latency, mobile issues), or fundamental mismatch between traffic expectations and qualification requirements.
How do I measure ROI from conversational AI qualification?
Key metrics include: cost per qualified lead (compare to pre-implementation cost), qualified lead volume (should increase from 24/7 coverage), response time (should decrease dramatically), and downstream conversion rate (should improve from better qualification and faster response). Connect qualification events to CRM outcomes to track revenue attribution. Budget 2-3 months for meaningful trend establishment.
Should I use GPT-4 or GPT-3.5 for qualification?
GPT-4 provides superior reasoning, instruction-following, and handling of complex scenarios – appropriate for high-value lead segments, complex products, or qualification requiring nuanced judgment. GPT-3.5 handles simpler qualification flows at roughly 10% the cost – appropriate for high-volume, straightforward qualification. Many implementations use GPT-4 for priority segments and GPT-3.5 for volume segments.
What are the biggest implementation mistakes to avoid?
Common failures include: inadequate prompt engineering (minimal instructions producing inconsistent results), missing CRM integration (qualification data that never reaches sales workflow), poor handoff experience (prospects repeating information or waiting in queues), and no feedback loop (no measurement enabling optimization). Invest in each area proportionally rather than focusing exclusively on conversation design.
Key Takeaways
Conversational AI solves the qualification velocity problem. Lead value decays 10% per hour without engagement. Human qualification cannot respond instantly at scale. ChatGPT-powered qualification engages prospects in seconds, 24/7, capturing value that time-delayed human response would lose.
Technical implementation determines success or failure. ChatGPT API access is necessary but not sufficient. Effective implementation requires integration architecture connecting conversation to CRM, lead distribution, and handoff systems. Organizations achieving strong results invest more in integration than in conversation design.
Prompt engineering is the hidden differentiator. The same ChatGPT model produces dramatically different results based on prompt quality. Comprehensive prompts including role definition, behavioral guidelines, qualification criteria, guardrails, and format specification outperform minimal instructions by wide margins. Budget 20-40 hours for initial development and ongoing refinement.
Conversation design must feel natural, not mechanical. The advantage of LLMs over decision-tree chatbots is natural conversation handling. Implementations that force rigid qualification flows waste this capability. Design for conversation that accomplishes qualification objectives rather than for form-filling disguised as chat.
Handoff experience often determines overall success. Excellent AI qualification followed by poor human handoff destroys value. Context transfer, expectation management, and seamless transition matter as much as conversation quality. Test handoff from prospect perspective, not just technical function.
Economics favor conversational AI at scale. At sufficient volume (typically 500+ leads monthly), conversational AI qualification costs 80-95% less than human qualification while providing instant 24/7 response. The crossover point depends on current qualification costs and implementation complexity.
Compliance requirements apply. AI involvement requires disclosure. Data collection triggers privacy obligations. Conversation transcripts may have retention requirements. Outbound calling following AI qualification requires appropriate consent. Build compliance into implementation design rather than addressing retroactively.
Measurement enables optimization. Track conversation-level metrics (completion rate, qualification rate, escalation rate) and business impact metrics (cost per qualified lead, downstream conversion, revenue per conversation). Connect qualification events to CRM outcomes. Review transcripts systematically to identify improvement opportunities.
Sources
-
arXiv: Language Models are Few-Shot Learners (GPT-3) - OpenAI’s foundational paper on large language models that underpin ChatGPT’s conversational capabilities.
-
OpenAI: GPT-4 Technical Report - Technical documentation on GPT-4 capabilities, safety features, and performance benchmarks referenced for model comparison.
-
HubSpot Marketing Statistics - Research supporting claims about lead response timing and speed-to-contact conversion impact.
-
Salesforce Research Reports - Customer experience research including self-service preferences and response time expectations.
-
Grand View Research: Chatbot Market Analysis - Market sizing data for the global chatbot industry referenced in industry growth projections.
Those who master conversational AI qualification in 2025 will compound that advantage over the following years. As the technology matures and adoption spreads, early implementations become training data for optimization that late adopters cannot replicate. The window for building conversational qualification infrastructure is now – not because the technology is new, but because the implementation learning curves create lasting competitive advantage. Your leads are waiting. Every minute without response, value decays. The question is not whether to implement conversational qualification, but how quickly you can achieve effective deployment.