How to implement pre-purchase validation that prevents bad leads from entering your pipeline, reduces return rates by 60-80%, and protects your buyer relationships through systematic quality enforcement.
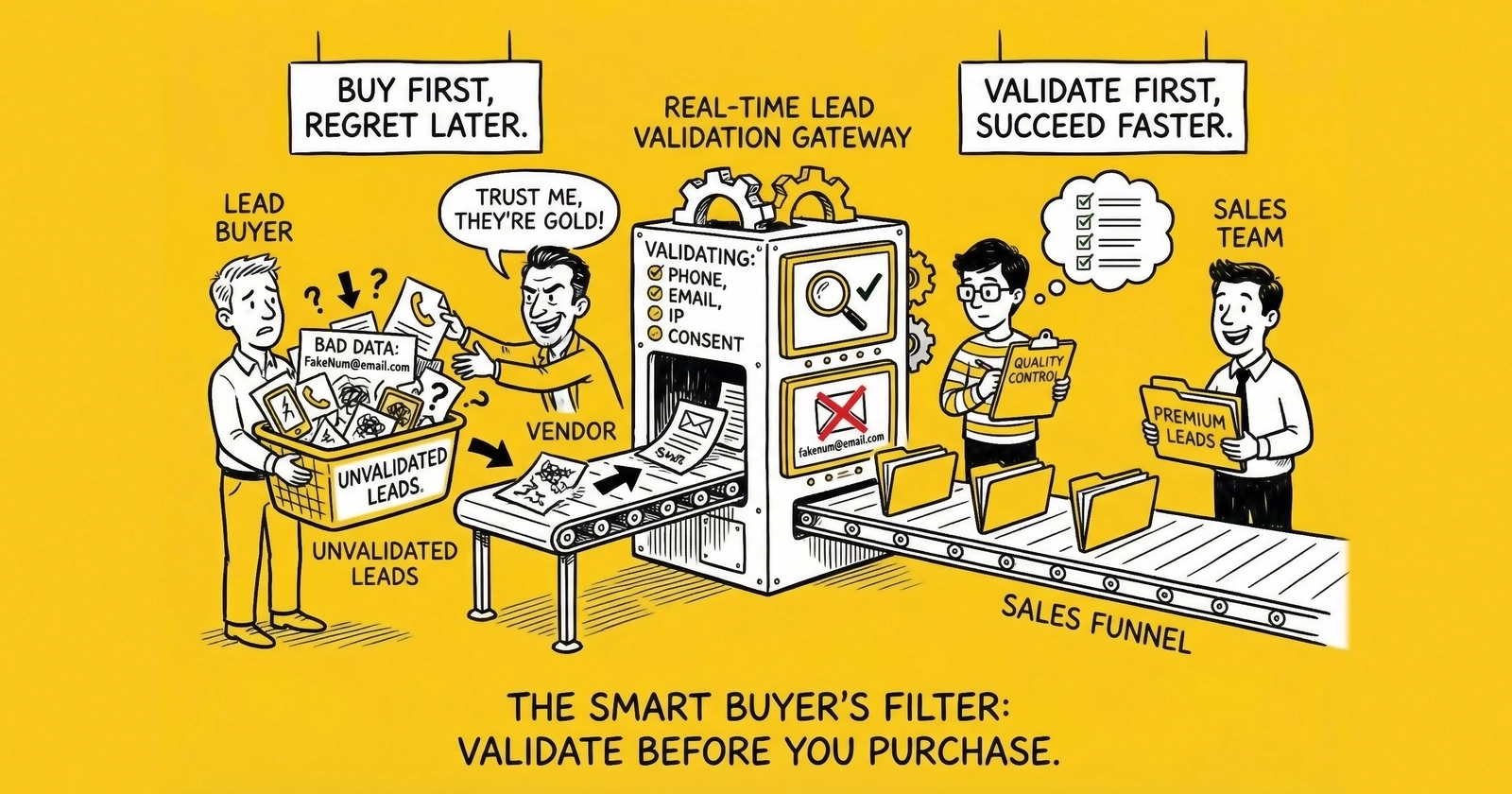
Every lead buyer has experienced the frustration: you purchase a batch of leads that looked promising on paper, only to discover that 20% contain disconnected phone numbers, 15% bounce when you send emails, and another 10% trigger fraud alerts during contact attempts. By the time you identify these problems, you’ve already paid for worthless leads, wasted sales resources attempting contact, and strained your relationship with the vendor.
Real-time lead validation before purchase changes this dynamic fundamentally. Instead of discovering quality problems after the transaction, you verify lead data at the moment of acquisition, before you commit to payment. Invalid leads never enter your pipeline. Fraudulent submissions never reach your sales team. Your return rate drops from industry average (15-25%) to best-in-class (3-8%).
This is not theoretical. The technology exists today, the economics overwhelmingly favor implementation, and the operational benefits compound over time. This guide covers everything you need to implement real-time validation: the technology stack, the integration patterns, the vendor landscape, and the optimization strategies that separate professional operations from amateur ones.
What Is Real-Time Lead Validation?
Real-time lead validation is the systematic verification of lead data at the moment of transaction, before purchase commitment. Unlike post-purchase validation (which identifies problems after you’ve paid), real-time validation enables you to reject bad leads before they enter your system and before you owe money for them.
The validation occurs during the transaction window, which depends on your lead acquisition method:
For ping/post systems: Validation happens during the bid evaluation phase. When you receive a ping containing partial lead data, you evaluate not just whether the lead matches your targeting criteria, but whether the underlying data passes quality checks. Your bid response (or rejection) reflects both targeting match and validation results.
For direct post delivery: Validation occurs during the acceptance window. When a lead arrives via API, you have a contractual window (typically 5-30 seconds) to verify data and return an accept or reject response. Validation runs during this window.
For batch file delivery: While less common in modern operations, batch validation happens after file receipt but before payment processing. You validate the entire file and pay only for leads that pass your quality thresholds.
The distinction between real-time and post-purchase validation is critical:
| Aspect | Real-Time Validation | Post-Purchase Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Before payment | After payment |
| Bad lead cost | Zero | Full lead price + return friction |
| Return process | Not required | Dispute, documentation, refund request |
| Vendor relationship | Protected | Strained by return volume |
| Sales team impact | Never sees bad leads | Wastes time on invalid contacts |
| Data quality | Consistently high | Variable until scrubbed |
The goal is simple: never pay for a lead you know to be invalid. Real-time validation makes this possible.
The Business Case: Why Real-Time Validation Pays for Itself
Before diving into implementation, let’s establish why real-time validation represents one of the highest-ROI investments available to lead buyers. The math is compelling across multiple dimensions.
Direct Cost Savings
Consider a lead buyer purchasing 5,000 leads monthly at $40 average CPL. Industry research indicates that 25-30% of third-party leads contain validation issues. Without real-time validation:
Without Validation:
- Monthly lead spend: $200,000
- Invalid lead rate: 25%
- Invalid leads purchased: 1,250
- Direct loss on invalid leads: $50,000
- Return recovery (assuming 60% success rate): $30,000
- Net loss: $20,000 per month ($240,000 annually)
With Real-Time Validation:
- Monthly lead spend: $200,000
- Validation cost ($0.10/lead): $500
- Invalid leads rejected before purchase: 1,250
- Valid leads purchased: 3,750
- Actual spend on valid leads: $150,000
- Net savings: $49,500 per month
The validation cost of $500 prevents $50,000 in losses. That represents a 100:1 return on investment when considering the full invalid lead cost. Even accounting for partial return recovery, the economics overwhelmingly favor pre-purchase validation.
Indirect Cost Savings
Beyond direct lead costs, validation eliminates hidden expenses that erode margins:
Sales team efficiency. Every invalid lead represents wasted sales activity. If an agent spends 8 minutes per lead attempt (dialing, leaving voicemail, documenting), 1,250 invalid leads consume 167 hours of sales time monthly. At $25/hour fully loaded cost, that represents $4,175 in wasted labor.
Opportunity cost. While agents attempt contact on dead leads, valid leads in queue age and decay. Research shows lead conversion drops 10% per hour without contact. Invalid leads don’t just cost money directly; they reduce conversion on your valid leads by consuming response capacity.
System overhead. Invalid leads pollute your CRM, skew reporting metrics, and require eventual cleanup. The administrative burden of managing returns, documenting disputes, and reconciling billing adds operational complexity that validation eliminates.
Reputation protection. Buyers with high return rates develop reputations that affect their market position. Premium lead sources prefer working with buyers who maintain clean operations. High-quality validation enables you to maintain relationships that matter.
Quality Threshold Enforcement
Real-time validation enables quality enforcement that post-purchase review cannot achieve. You can establish minimum quality thresholds and reject any lead that fails to meet them. Phone numbers must be valid, connected, and match claimed line type. Email addresses must be deliverable and not disposable. Physical addresses must verify to CASS standards. IP addresses must originate from expected geography, and behavioral signals must pass fraud detection thresholds.
These requirements become enforceable when validation occurs before purchase. The vendor cannot deliver leads that fail your validation because your system rejects them automatically.
The Real-Time Validation Technology Stack
With the business case established, the next question is implementation. Effective real-time validation requires multiple verification layers working in concert. No single check catches all problems. Defense in depth, with each layer catching issues the previous layers missed, delivers comprehensive protection.
Layer 1: Phone Number Validation
Phone validation is the foundation of lead quality verification. If you cannot contact a consumer, the lead has zero value regardless of other data quality. Comprehensive phone validation includes:
Format verification confirms the number follows valid patterns: correct digit count for the country code, valid area code assignment, and no obviously invalid sequences (555-xxx-xxxx, 000-000-0000). This is instantaneous and essentially free. Every validation stack should include it as the first gate.
Line type detection identifies whether the number connects to a mobile phone, landline, or VoIP service. This matters for multiple reasons. TCPA compliance requires different consent for mobile versus landline, creating regulatory implications. Mobile phones have higher contact rates because consumers carry them constantly. Non-fixed VoIP numbers from services like Google Voice and TextNow correlate with 3-5x higher fraud rates, leading many buyers to reject or discount non-fixed VoIP entirely.
Carrier lookup identifies which carrier currently owns the number, whether it has been ported, and its country of origin. Prepaid carriers and certain VoIP providers correlate with higher fraud. Numbers ported multiple times may indicate recycling or fraud. International carriers appearing on domestic leads signal data manipulation.
Disconnected number detection uses carrier databases to identify numbers no longer in service. This catches numbers that passed format validation but will fail contact attempts.
Reassigned number database checking addresses a specific compliance risk. A phone number previously belonging to one consumer may have been reassigned to someone who never consented to contact. The FCC’s Reassigned Numbers Database helps identify these situations.
DNC registry screening checks against the National Do Not Call Registry (240+ million numbers) and state-specific DNC lists. This is both a quality measure and a compliance requirement.
Phone validation vendor pricing (2024-2025):
| Service Level | Per-Lead Cost | What You Get |
|---|---|---|
| Format only | Free-$0.001 | Digit count, area code validity |
| Carrier lookup | $0.005-$0.01 | Carrier name, port status |
| Line type detection | $0.007-$0.015 | Mobile/landline/VoIP classification |
| DNC screening | $0.001-$0.005 | Registry matching |
| Full phone validation | $0.02-$0.05 | All of the above plus caller ID |
Layer 2: Email Validation
Email validation prevents bounces, protects sender reputation, and identifies low-intent submissions. A high bounce rate (above 2%) damages your sender reputation with ESPs, potentially blocking your entire domain from reaching inboxes.
Syntax and domain verification catches obvious errors: missing @ symbols, invalid characters, impossible domain formats. Domain verification confirms the domain exists and has mail exchange (MX) servers configured. Approximately 3-5% of form submissions contain domain typos that MX checking catches.
Mailbox verification (SMTP verification) checks whether the specific email address exists at the verified domain. This is the most comprehensive email validation step, confirming the mailbox accepts mail without actually sending a message.
Disposable email detection identifies temporary email services (Mailinator, Guerrilla Mail, 10MinuteMail, and hundreds of others) that indicate low-intent users trying to avoid follow-up contact. Quality validation services maintain databases of 100,000+ known disposable domains.
Spam trap detection identifies addresses created specifically to catch spammers. Sending to spam traps instantly damages sender reputation.
Catch-all domain handling addresses domains configured to accept mail for any address. For these domains, SMTP verification cannot confirm whether the specific address is valid. Your validation logic should flag these for special handling.
Email validation vendor pricing (2024-2025):
| Vendor | Price Per Email | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ZeroBounce | $0.008-$0.01 | 99%+ accuracy guarantee |
| NeverBounce | $0.003-$0.008 | Volume discounts, delivery guarantee |
| Hunter.io | $0.01-$0.017 | Credit-based system |
| Clearout | $0.004-$0.01 | Includes enrichment features |
Layer 3: Address Validation
Physical address validation matters most for verticals tied to specific properties or geographic service areas: home services, solar installation, mortgage refinancing, real estate, and insurance.
USPS CASS certification standardizes and validates mailing addresses against the USPS database. CASS-certified addresses have been verified to follow proper formatting and represent deliverable locations. The process corrects common errors (misspellings, incorrect zip codes, missing apartment numbers) and standardizes formatting.
Geocoding converts addresses to latitude/longitude coordinates. This confirms the address exists at a specific location and enables geographic validation. For property-related verticals, geocoding supports roof analysis (solar), service area confirmation (home services), and rating territory determination (insurance).
Property data appending adds characteristics like estimated home value, square footage, year built, lot size, and ownership status. This data supports both validation (a “homeowner” lead listing a rental property raises quality questions) and qualification (a solar lead for a heavily shaded property won’t convert).
Address validation vendor pricing (2024-2025):
| Vendor | Per-Lookup Cost | Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Smarty (SmartyStreets) | $0.01-$0.04 | CASS-certified, 1,000 free/month |
| Loqate | $0.041-$0.047 | US/Canada, includes geocoding |
| Melissa | $0.01-$0.05 | Enterprise pricing, 240+ countries |
Layer 4: Fraud Detection
Validation catches bad data. Fraud detection catches bad actors. These are different problems requiring different solutions. Fraudsters continuously evolve their techniques, and effective detection requires multiple overlapping signals.
IP analysis examines the network characteristics of form submissions. The system checks geographic consistency to determine whether IP location matches the claimed address. It performs VPN and proxy detection to identify users hiding their true location. Data center detection reveals whether traffic originates from hosting providers rather than residential networks. IP reputation scoring checks whether this IP has been associated with previous fraud.
Data center IPs are not always fraudulent, but they warrant additional scrutiny. When datacenter IP combines with other risk signals, fraud probability increases substantially.
Device fingerprinting creates a unique identifier for each device based on browser configuration, installed plugins, screen resolution, system fonts, timezone settings, and dozens of other attributes. A legitimate consumer typically uses one or two devices to submit forms. A fraudster submitting hundreds of fake leads needs to mask this, and device fingerprinting catches the attempt.
Behavioral analysis examines how users complete forms, not just what they submit. Form completion time provides a critical signal: completing a 10-field form in 3 seconds indicates automation. Typing patterns differ between humans and bots, with humans typing in irregular rhythms while bots type with machine precision. Mouse movement reveals intent as well, since humans move cursors in curved paths with micro-corrections while bots move in straight lines. Field focus patterns also diverge; humans tab between fields while bots often fill all fields simultaneously.
Velocity checking examines submission frequency to identify patterns inconsistent with organic behavior. IP-based velocity tracks multiple submissions from a single IP in short timeframes. Device-based velocity flags the same device fingerprint appearing across multiple submissions. Data-based velocity catches the same phone number or email appearing in multiple submissions.
Fraud detection vendor pricing (2024-2025):
| Vendor | Per-Lead Cost | Specialty |
|---|---|---|
| HUMAN (formerly White Ops) | $0.02-$0.10 | Bot detection |
| DataDome | Custom | Real-time protection |
| Fraudlogix | $0.01-$0.05 | Lead generation focus |
| Fingerprint.js | $0.001-$0.01 | Device identification |
Layer 5: Consent Verification
For TCPA compliance, validating consent documentation is as important as validating contact data. Consent verification services confirm that proper consent was captured and documented.
TrustedForm captures the actual form submission session, creating a certificate that includes session replay, consent language displayed, timestamp, IP address, and page content at time of submission. Certificates provide litigation-grade evidence of consent. See the TrustedForm vs Jornaya comparison for a detailed breakdown of each platform’s strengths.
Jornaya (now Verisk) tracks consumer journey across publishers, providing lead intelligence that includes submission patterns, multi-form behavior, and consent documentation.
Consent verification pricing (2024-2025):
| Vendor | Per-Lead Cost | What You Get |
|---|---|---|
| TrustedForm | $0.25-$0.50 | Session replay, consent certificate |
| Jornaya | $0.10-$0.30 | Journey tracking, lead intelligence |
Integration Patterns for Real-Time Validation
Understanding what to validate is only half the challenge. How you integrate validation depends on your lead acquisition method. The three primary patterns are ping/post integration, direct post validation, and API middleware implementation.
Ping/Post Integration
In ping/post systems, validation occurs during the bid evaluation phase. When you receive a ping containing partial lead data, you evaluate targeting match across geography, vertical, and attributes while simultaneously running available validation checks on the ping data. Based on these results, you calculate a quality score and adjust your bid price accordingly. Your bid response (or rejection) reflects both targeting match and quality assessment.
The challenge is that ping data is intentionally limited. You cannot validate phone numbers or emails during the ping phase because that data is not transmitted, protecting consumer privacy until purchase commitment. Your ping-phase validation is therefore limited to geographic validation comparing IP location versus claimed zip, source reputation scoring based on historical quality from each publisher, device and behavioral signals when available in ping metadata, and attribute consistency checks.
Full validation occurs during the post phase. When you win the auction and receive complete lead data, you have a brief window (typically 500-1000ms) to validate the phone number for line type, carrier, and disconnected status. You verify email deliverability and check for disposable addresses. You validate the address against CASS certification and geocoding standards. You run fraud detection on the full data set and check consent documentation. Finally, you return an accept or reject response within the timeout window.
Post rejection triggers waterfall-on-failure logic on the seller’s platform. Well-implemented waterfall systems recover 20-40% of leads that initial winners reject. Real-time bidding technology provides comprehensive coverage of ping/post mechanics and auction dynamics.
Direct Post Validation
For leads delivered via direct API post (not auction-based), validation occurs during the acceptance window. Your API endpoint receives the complete lead, runs all validation checks, and returns an accept or reject response within the contractual timeout.
The typical direct post flow begins when a lead arrives via HTTPS POST to your endpoint. Your system parses and logs the raw submission, then validation checks execute in parallel across phone, email, address, and fraud detection. Results aggregate into an accept or reject decision, and the response returns within the timeout window (typically 5-30 seconds). Accepted leads enter your CRM while rejected leads return to the sender.
The key architectural consideration is that validation must complete within the timeout. If your validation stack takes 10 seconds but your timeout is 5 seconds, you will timeout and potentially receive leads you would have rejected.
Performance optimization requires several strategies working together. Parallel execution runs phone, email, and address validation simultaneously rather than sequentially. Timeout budgeting allocates specific time to each validation step and aborts if the budget is exceeded. Caching stores repeated lookups so the same phone number appearing in multiple leads does not require redundant verification. Vendor failover ensures that if your primary validator times out, you fall back to a secondary service or accept with a flag for follow-up verification.
API Middleware Implementation
For complex validation requirements, middleware platforms aggregate multiple validation services into a single API call. Rather than integrating directly with phone, email, address, and fraud detection vendors, you integrate once with a middleware platform that handles the complexity.
LeadConduit (from ActiveProspect) is the industry-leading middleware for lead validation. It provides pre-built integrations with dozens of validation vendors, configurable validation workflows, real-time decision logic, consent verification through TrustedForm integration, and delivery routing post-validation.
The advantages of middleware are significant. You gain a single integration point versus multiple vendor APIs. The vendor-agnostic flexibility allows you to swap providers without code changes. Built-in logging and reporting simplify operations, and compliance documentation comes standard.
The disadvantages merit consideration as well. Middleware adds per-lead cost for the additional layer. You become dependent on the middleware platform’s uptime. There is also potential latency added by intermediate processing that you must account for in your timeout budgets.
For high-volume operations (50,000+ leads monthly), the middleware cost typically represents 2-5% of lead spend while providing significant operational efficiency.
Building Your Validation Rules Engine
With the technology stack and integration patterns defined, the next step is building the logic layer. Validation technology is only half the equation. Equally important is the logic that determines which leads to accept or reject based on validation results. Your rules engine translates validation outputs into business decisions.
Quality Scoring Framework
Rather than treating validation as binary (pass/fail), sophisticated buyers implement quality scoring that weighs multiple factors:
Phone validation score (0-25 points):
- Valid format: +5
- Non-VoIP line type: +5
- Major carrier: +5
- Not on DNC: +5
- Number age 2+ years: +5
Email validation score (0-20 points):
- Deliverable status: +10
- Not disposable: +5
- Not role-based (info@, sales@): +5
Address validation score (0-15 points):
- CASS certified: +10
- Geocodes to rooftop level: +5
Fraud detection score (0-25 points):
- Residential IP: +10
- Geographic match (IP vs claimed location): +5
- Device fingerprint clean: +5
- Behavioral signals pass: +5
Source quality score (0-15 points):
- Historical conversion rate above benchmark: +5
- Historical contact rate above 60%: +5
- Historical return rate below 10%: +5
Total quality score: 0-100 points
Your acceptance threshold becomes a business decision. A threshold of 70 points accepts high-quality leads while rejecting the bottom 30%. Adjusting the threshold balances volume against quality based on your conversion economics.
Tiered Acceptance Logic
Quality scores enable tiered acceptance that goes beyond binary accept/reject decisions.
Tier 1 (85-100 points) represents premium acceptance. Accept these leads immediately, route them to your best sales resources, and pay the full negotiated price. These are your highest-confidence opportunities.
Tier 2 (70-84 points) represents standard acceptance. Accept these leads with a monitoring flag, route them to standard processing, and pay full price. They meet your quality threshold but warrant tracking.
Tier 3 (50-69 points) represents conditional acceptance. If your contract permits, accept these leads at a discounted price reflecting their elevated risk. Otherwise, reject and log for analysis to understand what drives leads into this category.
Tier 4 (0-49 points) triggers automatic rejection. Reject with a reason code, log for source quality tracking, and flag repeated patterns for vendor discussion. These leads fail to meet minimum standards.
This tiered approach enables nuanced decisions that optimize value rather than forcing binary accept/reject logic.
Exception Handling
Validation systems must handle edge cases gracefully.
Validation timeout requires a decision when validation services do not respond within your budget. You can accept with a flag, risking acceptance of a bad lead. You can reject, risking rejection of a good lead. Or you can implement a hybrid approach that accepts if source reputation is strong while rejecting leads from unknown sources.
Partial validation failure occurs when some services respond but others do not. If phone validates but email service is down, do you accept? Your rules should define acceptable partial validation scenarios and flag leads for follow-up when full validation was not possible.
Conflicting signals create ambiguity. If phone validates but fraud score is borderline, which wins? Weighting in your scoring model determines outcomes for most cases, but edge cases may require manual review queues where human judgment resolves conflicts.
Novel patterns emerge as fraudsters adapt. Leads that pass all validation but fail conversion at unusual rates should trigger investigation. Your rules engine should evolve based on outcome data, not remain static.
Vendor Selection and Comparison
With the rules engine framework established, the question becomes which vendors to select. The validation technology market includes specialized point solutions and integrated platforms. Your choice depends on volume, vertical requirements, technical capability, and budget.
Comprehensive Validation Platforms
Melissa provides full-stack validation covering phone, email, address, and identity with 240+ country coverage. Strong for operations requiring international validation or complex address handling. Enterprise pricing typically runs $0.01-$0.10 per multi-field validation depending on volume and features.
Neustar (TransUnion) offers carrier-grade phone validation with identity verification and TCPA compliance tools. Particularly strong for high-volume telecommunications and financial services verticals. Enterprise sales required for pricing.
Ekata (Mastercard subsidiary) specializes in identity verification with phone, email, address, and IP analysis. Machine learning fraud scoring draws on global identity graph. Enterprise pricing.
Point Solutions by Category
For phone validation, Twilio Lookup offers a developer-friendly API at $0.008 per lookup for line type. Trestle (formerly Payfone) specializes in phone intelligence and ownership verification. Numverify provides global coverage across 232 countries starting at $14.99 per month.
For email validation, ZeroBounce offers a 99%+ accuracy guarantee at $0.008-$0.01 per email. NeverBounce provides a delivery guarantee refund policy at $0.003-$0.008 per email. Hunter.io uses a credit-based system and includes email finding capabilities.
For address validation, Smarty (SmartyStreets) provides CASS-certified validation with a free tier available. Loqate covers 250+ countries and includes geocoding.
For fraud detection, HUMAN provides enterprise bot detection. Fingerprint.js specializes in device identification with a freemium model available. DataDome offers real-time bot management.
Middleware Platforms
LeadConduit (ActiveProspect): Industry standard for lead validation middleware. Pre-built integrations with 40+ vendors, configurable workflows, consent verification. Volume-based pricing.
LeadsPedia: Hybrid lead distribution and validation platform. Built-in fraud detection and verification. SaaS pricing $450-$2,500/month.
Boberdoo: Enterprise lead distribution with integrated validation capabilities. Particularly strong for insurance vertical. Starts around $1,000/month plus transaction fees.
Build vs. Buy Analysis
Building validation capabilities in-house requires significant engineering investment. Engineering time runs 6-12 months for comprehensive implementation. Ongoing maintenance typically consumes 20-30% of initial development cost annually. Data source licensing varies by vendor but often runs $10,000-$50,000+ annually. Infrastructure adds server costs, redundancy requirements, and monitoring overhead. The minimum viable build costs $100,000-$200,000 before data licensing.
For operations processing fewer than 100,000 leads monthly, vendor solutions almost always prove more economical. Above that scale, hybrid approaches (in-house for some functions, vendor for others) may optimize cost.
The build option makes sense when volume exceeds 500,000 leads monthly, when validation requirements are highly specialized, when an existing engineering team has relevant experience, or when data licensing can be negotiated at scale.
The buy option makes sense when volume is under 100,000 leads monthly, when requirements are standard, when fast implementation is a priority, or when engineering resources are limited.
Implementation Roadmap
Implementing real-time validation requires phased deployment to minimize disruption while building capability. This roadmap assumes a mid-market operation purchasing 10,000-50,000 leads monthly.
Phase 1: Foundation (Weeks 1-2)
The first phase establishes basic validation on highest-impact data points. You integrate phone line type detection to catch VoIP flags and email deliverability verification to catch bounces. Implement basic format validation client-side where possible. Configure acceptance timeout handling and build logging for validation results from day one.
This foundation phase typically achieves 10-15% rejection of obviously invalid leads at a validation cost of $0.02-$0.05 per lead.
Phase 2: Core Validation (Weeks 3-4)
The second phase builds comprehensive data validation across phone, email, and address. Add carrier lookup and DNC screening to your phone validation. Integrate disposable email detection. If relevant to your vertical, add CASS address standardization. This is also when you implement your quality scoring framework and configure tiered acceptance logic.
Phase 2 typically achieves an additional 8-12% rejection of invalid or high-risk leads, bringing your validation cost to $0.05-$0.12 per lead.
Phase 3: Fraud Detection (Weeks 5-6)
The third phase layers fraud detection on top of validated leads. Add IP intelligence covering geolocation and VPN detection. Integrate device fingerprinting. If available in your lead metadata, add behavioral analysis. Implement velocity checking and tune your fraud scoring thresholds based on initial results.
Fraud detection typically catches an additional 3-5% of fraudulent submissions that passed basic validation. Your total validation cost at this stage reaches $0.08-$0.15 per lead.
Phase 4: Optimization (Ongoing)
The fourth phase is never truly complete. Continuous improvement based on outcome data drives ongoing refinement. Correlate validation scores with conversion outcomes to understand which signals actually predict performance. Adjust scoring weights based on this performance data. A/B test acceptance thresholds to find the optimal balance between volume and quality. Evaluate new validation vendors as the market evolves. Build source-level quality dashboards that reveal which publishers deliver consistent quality and which require attention.
Track these key metrics to measure optimization progress: validation pass rate (target 70-85%), false positive rate measuring valid leads rejected as invalid, false negative rate measuring invalid leads passing validation, post-validation return rate (target under 5%), and contact rate on accepted leads (target 65% or higher).
Common Implementation Mistakes
Even with the right technology, vendors, and roadmap, validation implementation carries predictable pitfalls. Anticipating these issues prevents wasted effort and suboptimal results.
Mistake 1: Over-Rejecting Valid Leads
Aggressive validation thresholds can reject legitimate leads that would have converted. Every false positive costs you a potential customer.
The symptoms are clear: pass rate drops below 60% (meaning you reject more than you accept), vendors complain about your rejection rates, and volume drops despite adequate supply in the market.
Prevention requires systematic analysis. Analyze rejected leads for patterns that might indicate over-aggressive thresholds. Sample-verify rejected leads to measure your actual false positive rate. Implement tiered acceptance rather than binary rejection to capture borderline leads at appropriate terms. Start with lenient thresholds and tighten based on data rather than assumptions.
Mistake 2: Timeout Configuration Errors
If validation takes longer than your acceptance window, you either timeout (miss the lead) or accept without full validation (defeat the purpose).
The symptoms manifest as high timeout rates on validation services, leads accepted without validation flags in your system, and latency complaints from lead sources whose systems are waiting on your response.
Prevention starts before integration. Benchmark validation service response times during evaluation, not after commitment. Allocate timeout budgets per validation step so slow components do not consume the entire window. Implement parallel rather than sequential validation to maximize throughput. Configure vendor failover for timeout scenarios so a slow primary does not block your entire operation.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Source-Level Quality
Aggregate validation metrics mask source-specific problems. A 10% overall rejection rate might include one source at 3% and another at 30%.
The symptoms appear as consistently mediocre quality despite validation investment, return rates that do not improve proportionally to what your validation should catch, and ongoing vendor relationship friction that seems disconnected from your overall metrics.
Prevention requires granular tracking. Track validation results by source and publisher, not just in aggregate. Set source-specific quality thresholds that hold each partner accountable. Flag sources exceeding rejection benchmarks for review and discussion. Use source quality data in pricing negotiations, rewarding high-quality partners and adjusting terms for problematic ones.
Mistake 4: Static Threshold Management
Market conditions change. Fraud techniques evolve. Thresholds set at implementation may not remain optimal.
The symptoms emerge over time: conversion rates declining on accepted leads that your validation approved, new fraud patterns appearing in post-acceptance analysis that your thresholds missed, and validation costs rising without proportional benefit as fraudsters adapt to your detection methods.
Prevention requires ongoing attention. Schedule quarterly threshold reviews as a mandatory calendar item. Correlate validation scores with conversion outcomes to identify when scores stop predicting performance. Monitor industry fraud trend reports to anticipate emerging threats. Maintain vendor relationships for threat intelligence that informs your threshold adjustments.
Mistake 5: Incomplete Data Logging
Without comprehensive logging, you cannot analyze validation effectiveness or diagnose problems.
The symptoms become apparent when you need data that does not exist: you cannot calculate false positive or negative rates because you did not preserve the necessary inputs, you cannot correlate validation with conversion because the data lives in disconnected systems, and you cannot support dispute resolution with vendors because you lack the audit trail to prove your case.
Prevention must begin at implementation. Log raw validation inputs and outputs for every lead processed. Preserve validation scores with lead records so conversion analysis can access them. Maintain an audit trail for compliance that satisfies regulatory requirements. Build reporting dashboards from day one rather than retrofitting them later when you realize you need visibility.
Measuring Validation Effectiveness
Having avoided the common mistakes, the final step is establishing measurement frameworks. You cannot improve what you cannot measure. Validation effectiveness requires tracking metrics across multiple dimensions.
Operational Metrics
Pass rate: Percentage of leads passing all validation checks. Target: 70-85% depending on source quality. Below 60% suggests over-rejection; above 90% suggests under-validation.
Rejection distribution: Breakdown of rejections by reason (phone invalid, email bounced, fraud detected, etc.). Identifies which validation layers catch the most issues.
Validation latency: Time from lead receipt to validation completion. Target: under 500ms for most operations. Monitor for degradation.
Timeout rate: Percentage of validation requests that timeout. Target: under 1%. Higher rates indicate infrastructure or vendor issues.
Quality Metrics
Post-validation return rate: Returns on leads that passed validation. This is your ultimate quality measure. Target: under 5% (significantly below the 15-25% industry average for unvalidated leads).
Contact rate: Percentage of validated leads where you successfully reach the consumer. Target: 65-85% depending on vertical. If validation is working, contact rates should exceed industry benchmarks.
Fraud detection rate: Percentage of leads flagged by fraud detection. Monitor for trends rather than absolute targets. Sudden spikes indicate either source problems or new fraud patterns.
False positive rate: Valid leads incorrectly rejected. Measure by sampling rejected leads. Target: under 2%.
Economic Metrics
Validation cost per accepted lead: Total validation spend divided by accepted leads. This is higher than per-lead validation cost because you’re paying to validate rejected leads too.
Cost per valid lead: Lead price plus validation cost. Compare against unvalidated lead price plus estimated return/waste cost.
Return on validation investment: (Savings from prevented bad leads) / (Validation cost). Target: 10:1 or higher.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is real-time lead validation and why is it important?
Real-time lead validation is the systematic verification of lead data at the moment of acquisition, before purchase commitment. Unlike post-purchase validation that identifies problems after payment, real-time validation enables you to reject invalid leads before they enter your system and before you owe money for them.
The importance comes from the economics: approximately 25-30% of third-party leads contain validation issues according to industry research. Without pre-purchase validation, you pay for worthless leads, waste sales resources attempting contact, and strain vendor relationships through return disputes. Real-time validation eliminates these costs by catching problems before they enter your pipeline.
How much does real-time lead validation cost per lead?
Basic validation (phone line type, email deliverability) costs $0.02-$0.05 per lead. Comprehensive validation (phone, email, address, fraud detection) costs $0.08-$0.15 per lead. Enterprise validation with identity verification and consent checking costs $0.15-$0.50 per lead.
The cost varies by vendor selection, volume discounts, and which validation layers you implement. Most operations find the optimal cost/benefit around $0.08-$0.12 per lead for full validation.
What validation checks should I implement first?
Prioritize based on impact. Phone line type detection should come first because it catches VoIP fraud signals and TCPA compliance issues. Email deliverability comes second, preventing bounces and identifying disposable addresses. DNC screening is third, addressing a compliance requirement for outbound calling. IP analysis rounds out the foundation, catching geographic mismatch and VPN/proxy usage.
These four checks catch the majority of validation issues at minimal cost. Add address validation and advanced fraud detection as Phase 2.
How does validation integrate with ping/post lead distribution?
In ping/post systems, validation occurs in two phases. During the ping phase, you validate what you can from partial data: IP analysis, source reputation, behavioral signals. During the post phase (after winning the auction), you validate full data: phone, email, address, consent documentation. Post-phase validation must complete within the acceptance timeout, typically 500-1000ms.
If post-phase validation fails, you reject the lead, triggering waterfall-on-failure logic that routes to the next bidder.
What return rate should I expect after implementing validation?
Well-implemented validation reduces return rates from industry average (15-25%) to best-in-class (3-8%). The exact improvement depends on your baseline quality, validation comprehensiveness, and threshold configuration.
Expect 60-80% reduction in return rates within 60 days of full validation implementation. Industry lead return rate benchmarks provide context for evaluating your performance. If you’re not seeing this improvement, audit your validation coverage and threshold settings.
How do I handle validation service timeouts?
Timeout handling requires a decision: accept with risk, reject with risk, or implement intelligent fallback.
Best practice: configure parallel validation to minimize timeout risk. If timeout occurs despite parallel execution, accept leads from high-reputation sources while rejecting leads from unknown or problematic sources. Log all timeout-accepted leads for post-hoc analysis.
Never let validation timeout increase your acceptance window beyond what sources expect. This causes technical failures in the delivery chain.
Should I build validation in-house or use vendors?
For operations under 100,000 leads monthly, vendor solutions are almost always more economical. The engineering investment ($100,000-$200,000+) and ongoing maintenance burden exceed vendor costs at this scale.
Consider building in-house when volume exceeds 500,000 monthly leads, validation requirements are highly specialized, or you have existing engineering capacity with relevant experience. Hybrid approaches (in-house for some functions, vendor for others) often work well for mid-large operations.
How do I measure validation effectiveness?
Track five key metrics. Pass rate should target 70-85%, adjusted based on source quality. Post-validation return rate should target under 5%. Contact rate on validated leads should target 65-85%. False positive rate should target under 2%. Validation ROI should target 10:1 or higher.
Compare validated lead performance against your historical unvalidated baseline. Validation should demonstrably improve contact rates, reduce returns, and increase conversion.
What is the difference between validation and lead scoring?
Validation confirms data accuracy: the phone number works, the email delivers, the address exists. It answers: “Is this lead real?”
Lead scoring predicts conversion likelihood based on attributes, behavior, and historical patterns. It answers: “Will this lead convert?”
Both are valuable, but they serve different purposes. Validation is table stakes; scoring enables prioritization. A lead can be validated (data is real) but low-scored (unlikely to convert) or vice versa.
How often should I review and adjust validation thresholds?
Quarterly reviews are the minimum acceptable cadence. Monthly reviews are better for high-volume operations.
Several triggers should prompt immediate review regardless of schedule. A significant change in return rates (up or down) indicates something has shifted. New fraud patterns appearing in accepted leads suggests thresholds need tightening. Vendor complaints about rejection rates may signal over-aggressive settings. Conversion rate changes not explained by other factors warrant investigation of validation’s role.
Validation effectiveness degrades as fraudsters adapt to detection. Continuous tuning maintains protection.
Key Takeaways
Real-time validation prevents bad leads from entering your system. Unlike post-purchase validation that identifies problems after payment, real-time validation enables rejection before commitment. This eliminates return disputes, protects vendor relationships, and stops wasted sales effort on invalid contacts.
The economics overwhelmingly favor implementation. At $0.08-$0.15 per lead, validation costs 0.2-0.4% of a $40 lead price while preventing 15-25% loss rates. ROI exceeds 50:1 for most operations. The only question is how comprehensive to make your validation stack.
Layer multiple validation types for defense in depth. No single check catches all problems. Phone validation, email verification, address standardization, and fraud detection each catch different issues. Combined, they provide comprehensive protection.
Integration pattern depends on your acquisition method. Ping/post systems validate during bid evaluation and post acceptance windows. Direct post validates during the acceptance timeout. Middleware platforms simplify multi-vendor integration for complex requirements.
Build quality scoring rather than binary accept/reject. Validation results should feed a scoring framework that enables tiered acceptance decisions. Premium scores route to best resources; borderline scores may accept at discount or route to review queues.
Measure effectiveness through outcome correlation. Track return rates, contact rates, and conversion on validated leads versus baseline. Validation should demonstrably improve these metrics. If it doesn’t, audit your implementation.
Vendor solutions beat in-house builds for most operations. The engineering investment and maintenance burden exceed vendor costs until you reach 500,000+ monthly leads. Start with vendors; consider building at scale.
Continuous tuning maintains protection. Fraud techniques evolve. Market conditions change. Thresholds set at implementation require ongoing adjustment based on outcome data and threat intelligence.
Statistics, vendor pricing, and regulatory information current as of late 2024 through early 2025. Vendor capabilities and pricing change frequently; verify directly with vendors for current information.